Shareholders Equity Definition, Formula, Calculate

Short-term debts generally fall into the current liabilities category, as these are things that a company is most likely to pay in the near future. Longer-term liabilities are ones that take longer than one year to clear. Return on equity is a measure that analysts use to determine how effectively a company uses equity to generate a profit. It is obtained by taking the net income of the business divided by the shareholders’ equity. Net income is the total revenue minus expenses and taxes that a company generates during a specific period.

What are the limits of shareholder equity as a metric?
There is a clear distinction between the book value of equity recorded on the balance sheet and the market value of equity according to the publicly traded stock market. The shareholders equity ratio, or “equity ratio”, is a method to ensure the amount of leverage used to fund the operations of a company is reasonable. From the viewpoint of shareholders, treasury stock is a discretionary decision made by management to indirectly compensate equity holders. Next, the “Retained Earnings” are the accumulated net profits (i.e. the “bottom line”) that the company holds onto as opposed to paying dividends to shareholders. real estate cash flow When companies issue shares of equity, the value recorded on the books is the par value (i.e. the face value) of the total outstanding shares (i.e. that have not been repurchased).
- Total equity shows the portion of the company’s assets that are owned outright by shareholders, which is crucial for evaluating ownership claims and control.
- In 2021, the share repurchases are assumed to be $5,000, which will be subtracted from the beginning balance.
- But if it’s negative, that means its debt and debt-like obligations outnumber its assets.
- Return on Equity (ROE) is the measure of a company’s annual return (net income) divided by the value of its total shareholders’ equity, expressed as a percentage (e.g., 12%).
- An analyst can generally use the balance sheet to calculate a lot of financial ratios that help determine how well a company is performing, how liquid or solvent a company is, and how efficient it is.
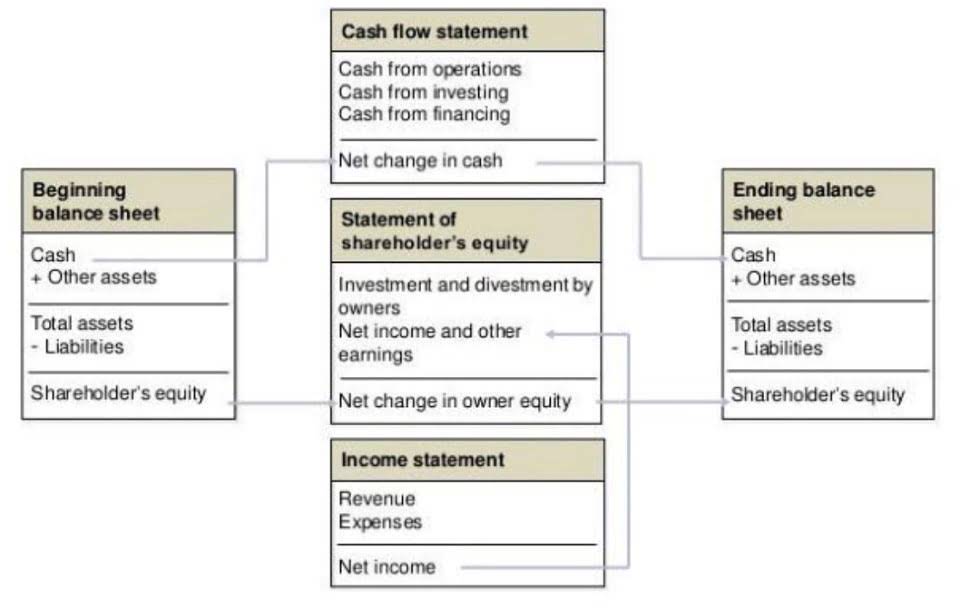
Understanding Shareholders’ Equity
That includes everything from cash and property to stock and equipment. It also owes $4 million in liabilities – things like loans, unpaid bills, and wages. These are usually available in annual reports, quarterly earnings reports , Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) announcements how to calculate total stockholders equity , or through financial data platforms.
- For that reason, investors often look at complementary metrics, such as ROIC, to help understand the full picture of the business.
- Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
- A negative shareholders’ equity means that shareholders will have nothing left when assets are liquidated and used to pay all debts owed.
- If the same assumptions are applied for the next year, the end-of-period shareholders equity balance in 2022 comes out to $700,000.
- There are many reasons why a company’s ROE may beat the historical average or fall short of it.
- Now that we’ve gone over the most frequent line items in the shareholders’ equity section on a balance sheet, we’ll create an example forecast model.
What is the Conceptual Meaning of Return on Equity (ROE)?

In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path. Includes non-AP obligations that are due within one year’s time or within one operating cycle for the company (whichever is longest). Notes payable may also have a long-term version, which includes notes with a maturity of more than one year. Accounts Payables, or AP, is the amount a company owes suppliers for items or services purchased on credit. As the company pays off its AP, it decreases along with an equal amount decrease to the cash account. Simply put, with ROE, investors can see if they’re getting a good return on their money, while a company can evaluate how efficiently they’re utilizing the firm’s equity.

Example Calculation of Total Equity

Whether negative stockholder’s equity is indicative of a larger problem usually requires taking a closer look at the company’s financials. Buybacks, for example, can push stockholders’ equity into negative territory in the short term but benefit the company financially in the long run. Unlike share prices, which react to headlines and sentiment, shareholder equity is based on the company’s actual balance sheet. It reflects what’s happening behind the scenes, not gross vs net just in the market.
- On the balance sheet, shareholders’ equity is broken up into three items – common shares, preferred shares, and retained earnings.
- Calculating stockholders’ equity can give investors a better idea of what assets might be left (and paid out to shareholders) once all outstanding liabilities or debts are satisfied.
- It represents the difference between total assets and total liabilities.
- For example, a positive change in plant, property, and equipment is equal to capital expenditure minus depreciation expense.
- Dividend recapitalization—if a company’s shareholders’ equity remains negative and continues to trend downward, it is a sign that the company could soon face insolvency.
- It also reflects a company’s dividend policy by showing its decision to pay profits earned as dividends to shareholders or reinvest the profits back into the company.
